Electric Bicycle Maintenance Tips (1)
Electric Bicycle Maintenance Tips
Tip ①: Avoid storing the battery in a discharged state
Tip ②: Conduct regular inspections
During use, if the electric bicycle’s range suddenly drops by more than ten kilometers in a short period, it is highly likely that at least one battery in the battery pack has developed faults such as internal circuit breakage, electrode plate softening, or detachment of active materials from the plates (resulting in short circuits). In such cases, you should promptly take the bicycle to a professional battery repair service for inspection, repair, and battery pack matching. This can relatively extend the service life of the battery pack and maximize cost savings.
Tip ③: Avoid high-current discharge
When starting the electric bicycle, carrying passengers, or climbing hills, use pedal assistance to minimize instantaneous high-current discharge. High-current discharge easily leads to the formation of lead sulfate crystals, which damage the physical properties of the battery’s electrode plates.
Tip ④: Master the correct charging time
During use, adjust the charging time according to actual conditions. Generally, batteries are charged at night, with an average charging time of approximately 8 hours. If the battery is only slightly discharged, it will be fully charged quickly; continuing to charge beyond this point will cause overcharging, leading to water loss and overheating of the battery, which reduces its service life. Therefore, the optimal time to charge the battery is when its discharge depth reaches 60%-70%. Adjust the charging frequency based on your actual usage to avoid damaging charging practices.
A discharged state refers to the situation where the battery is not recharged promptly after use. In this state, sulfation occurs—lead sulfate crystals attach to the electrode plates, blocking ion channels and preventing the battery from charging properly. The longer the battery is left idle in a discharged state, the more severe the damage will be.
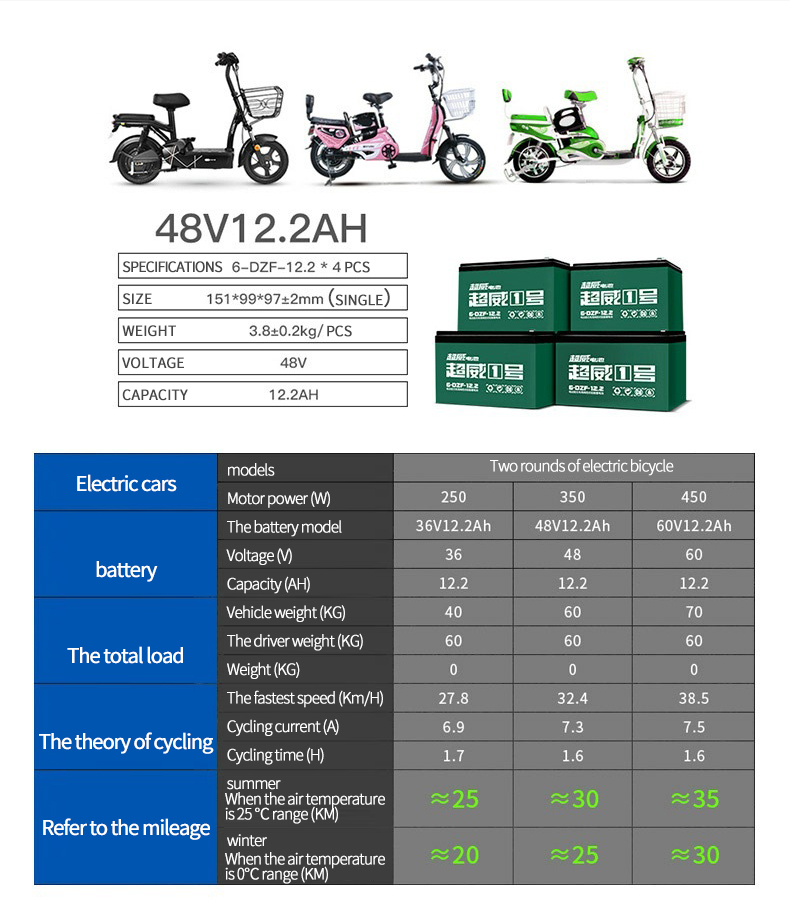
If you want to learn more about electric bicycle models and related knowledge, please contact us.
 Quick Troubleshooting for E-Bi
Quick Troubleshooting for E-Bi
 Quick Troubleshooting Guide fo
Quick Troubleshooting Guide fo
 Commuter E-Bike Buying Guide:
Commuter E-Bike Buying Guide:
 Comparison of Key Features of
Comparison of Key Features of
