Controllers are divided into sine wave controllers and square wave controllers. Sine wave controllers operate with low noise, while square wave controllers produce relatively high noise. The "number of tubes" in a controller refers to the quantity of power transistors (MOSFETs) inside it. Common specifications include 6-tube, 9-tube, 12-tube, 15-tube, etc. Generally, more tubes mean higher output power, but they also consume electrical energy faster. When the number of magnet steel pieces in the motor is ≥27-30, a module controller is usually recommended. Notably, 12-tube and 15-tube module controllers have the same external size.
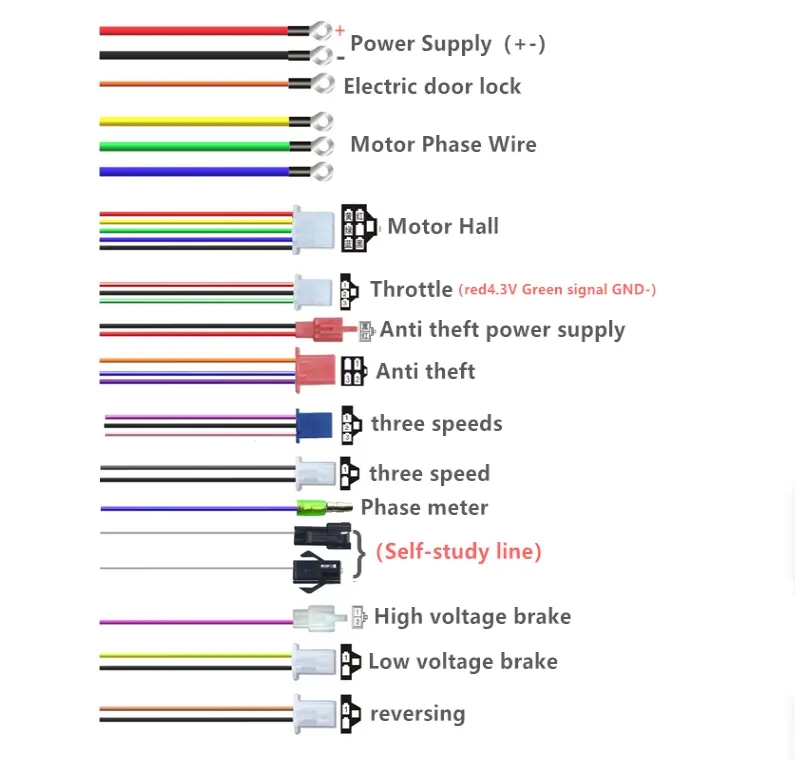

The "number of tubes" in a controller directly affects output power, load capacity, and energy consumption. Below are common specifications and their applicable scenarios:
6-tube Controller: Output power of approximately 250-350W with the lowest energy consumption. Suitable for daily commuting (e.g., electric bicycles, light electric vehicles) where long range and low-speed short-distance travel are prioritized.
9-tube Controller: Output power of approximately 400-500W, balancing power and range. Compatible with most household electric vehicles (load capacity ≤150kg, speed ≤40km/h) and is the most versatile specification.
12-tube Controller: Output power of approximately 600-800W with strong power. Ideal for medium-short distance heavy loads (e.g., carrying passengers, climbing slopes) or electric vehicles with speeds of 40-50km/h; moderate energy consumption.
15-tube Controller: Output power of approximately 800-1200W with high-power output. Suitable for high-speed electric vehicles, heavy-duty electric tricycles (load capacity ≥200kg), or scenarios involving frequent slope climbing. High energy consumption requires matching with a large-capacity battery.
⚠️ Important Note: The number of tubes must match the motor power—too few tubes may cause the controller to overheat and burn out, while too many tubes result in an "overpowered controller with an underpowered motor," leading to energy waste and shortened motor lifespan.
When the number of magnet steel pieces in the motor is ≥27-30, it is advisable to prioritize a module controller for the following key reasons:
High magnet steel motors generate stronger magnetic fields, requiring higher current stability and heat dissipation capabilities from the controller. Module controllers adopt an integrated design, offering better anti-interference performance and heat dissipation efficiency than ordinary discrete-component controllers. This prevents motor jitter or controller damage caused by current fluctuations.
12-tube and 15-tube module controllers share the same external dimensions, eliminating the need for additional installation space adjustments. The number of tubes can be selected based on motor power and usage scenarios (12-tube for medium-power high-magnet steel motors, 15-tube for high-power high-magnet steel motors).
Determine the "waveform type" first:
- Pursue low noise, comfort, and long range → Sine wave controller;
- Limited budget, low-speed short-distance use, or insensitive to noise → Square wave controller.
Check the "motor magnet steel":
- Number of magnet steel pieces <27 → Ordinary discrete controller (select the number of tubes based on power);
- Number of magnet steel pieces ≥27-30 → Module controller (12-tube/15-tube).
Finally, select the "number of tubes":
- Commuting and light loads → 6-tube/9-tube;
- Carrying passengers, climbing slopes, or medium power → 12-tube;
- Heavy loads, high speed, or high power → 15-tube.

 Quick Troubleshooting for E-Bi
Quick Troubleshooting for E-Bi
 Quick Troubleshooting Guide fo
Quick Troubleshooting Guide fo
 Commuter E-Bike Buying Guide:
Commuter E-Bike Buying Guide:
 Comparison of Key Features of
Comparison of Key Features of
